Frequently Asked Questions
Here’s a compilation of all the questions that you might have.
Still unsure? Contact us to find out if Zora Health’s services are right for you.
For Employers
Can I recommend my employer or company wellbeing team?
Yes. Zora Health provides support ranging from company-wide benefits, to organising activities with inclusive networks (e.g. women’s resource groups, male allyship groups) within your company.
Should you wish to refer your HR manager or resource group, simply fill in this form, and we will contact the relevant stakeholder. No personally identifiable information will be shared.
Who can use Zora Health’s services and how does my company benefit?
All employees are eligible, as the Zora Health solution covers all genders, ages, and life stages.
These range from male & female sexual health, menstrual health, male & female fertility health, pregnancy, personal & workplace support for new parents, parenting, menopause & andropause, and more. Employees need not have families nor be planning to have families to benefit from Zora Health’s platform.
Improved health outcomes go beyond fertility, reproductive and family wellbeing. Other areas such as mental wellbeing and productivity at work are positively impacted, while presenteeism and absenteeism are reduced.
Which regions are Zora Health available in?
Zora Health is available in more than 16 countries in regions such as Asia, Europe, North America, Latin America, Africa and the Middle East. We continue to expand our provider network; if you’d like to explore coverage for employees residing in any of these regions (including those not mentioned above), simply request a demo and a Zora Health representative will get in touch with you.
Is Integration with HRIS (HR info system) available?
Zora Health facilitates integration such as SSO (Single Sign-On), API and others. Please submit a request for a demo and we will be in touch to discuss the arrangements.
What is the pricing structure?
Different models are available in accordance with your needs, from subscription-based pricing for eligible populations to full coverage. Co-payment is also available.
For Clinics & Hospitals
Who are the clients that you work with?
Zora Health's user base includes women across all life stages, spanning: menstruation, fertility, pregnancy and delivery, paediatrics to menopause. We also have a large male user base who suffer from male infertility and andropause. These form our client base who may be seeking anything from ad-hoc massages and coaching to regular management of health conditions.
What types of clinical partners is Zora Health looking for?
We are particularly interested in partnering with healthcare groups, hospitals, and specialist fertility clinics. Relevant specialties include OBGYN (especially fertility specialists), Endocrinologists, Neonatal, Paediatrics and Radiologists. Adjacent specialties such as Oncology (for cervical cancer, breast cancer, testicular cancer, etc.) and Urology (for pelvic floor-related issues, post-pregnancy issues, or menopausal symptoms) are also of interest.
What are the benefits of partnering with Zora Health?
By partnering with Zora health, you gain access to a steady stream of pre-qualified patients, improving your clinic’s growth and conversion rates. Zora Health’s platform filters and nurtures users worldwide into high-intent prospects, significantly reducing your marketing and ad spend. Our care advocates also provide comprehensive out-of-clinic support, serving as layer to reduce patient-clinic friction and ultimately allowing your team to focus on higher-value work like delivering exceptional in-clinic care.
How do you determine which patients are referred to our clinic?
We use a patient-first approach, considering the patient’s specific health needs and preferences. Our platform then matches our users with the clinical partners that are best equipped to provide the required care.
What can we expect from Zora Health?
Our user base is global, comprising high-intent individuals as well as employees from large corporations with significant headcount spread across multiple countries, regions, and continents. This diversity allows us to refer a consistent stream of patients seeking a wide range of treatments, ensuring a steady flow of patients to your clinic.
How do we become a clinical partner with Zora Health?
Interested hospitals and fertility clinics can contact our Ecosystem and Partnerships team. Simply fill out this form on our website and book a video call with us. We’ll guide you through the onboarding process, which includes verifying credentials, understanding your specialities, and integrating your services with our platform.
For Businesses
Who are the patients that you work with?
Zora Health’s scope of services covers women across all life stages, spanning: menstruation, fertility, pregnancy and delivery, paediatrics to menopause. We also cover male infertility and andropause. These form our patient base who may be seeking anything from ad-hoc massages and coaching to regular management of chronic conditions.
What type of businesses is Zora Health looking to partner with?
We are keen to collaborate with businesses who can complement our holistic approach to health and wellness. We are looking for partnerships with Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) providers, confinement care centres, psychologists, nutritionists, and physical trainers. These partnerships help us provide comprehensive care that supports our users’ physical, mental, and emotional well-being across various life stages.
What are the benefits of partnering with Zora Health?
By partnering with Zora health, you gain access to a steady stream of pre-qualified patients, improving your businesses’ growth and conversion rates. Zora Health’s platform filters and nurtures users worldwide into high-intent prospects, significantly reducing your marketing and ad spend.
How do you determine which patients are referred to our business?
We use a patient-first approach, considering the patient’s specific health needs and preferences. Our platform then matches our patients with the partners that are best equipped to provide the required care.
What can we expect from working with Zora Health?
We have significant local user base in countries where we operate. These users come from are either high-intent individuals or employees from large corporations with significant headcount. This diversity allows us to refer a consistent stream of patients seeking a wide range of treatments, ensuring a steady flow of patients to your business.
How do we become a clinical partner with Zora Health?
Interested businesses can contact our Ecosystem and Partnerships team by filling out this form on our website and booking a video call with us. We’ll guide you through the onboarding process, which includes verifying credentials, understanding your specialities, and integrating your services with our platform.
For Individuals
What services do you offer?
Our comprehensive services include virtual and physical consultations, educational platforms, expert support and medical concierge services. Our global network spans over 100 partner clinics in 16 countries. Additionally, we facilitate health and educational workshops and roadshows to promote holistic wellness.
We are committed to supporting you through every stage of life, whether it's family planning, menopause, parenting support, hormonal health or addressing men's health concerns.
Which countries do you operate in?
We operate out of Asia but can serve anyone globally.
Just leave your contact and we can arrange for an initial introductory call.
Which countries can I do my treatment in?
We can connect you with any doctors globally.
What are the specific legal requirements in each country?
The specific legal requirements for IVF and egg freezing vary among South East Asian countries. In Singapore, for example, egg freezing is only allowed for medical reasons, and there are restrictions on the number of eggs that can be frozen. In Malaysia, there are no specific laws governing egg freezing, but there are guidelines that must be followed. In Thailand, egg freezing is allowed for medical reasons, but surrogacy is not legal. There is no legal framework in Indonesia for IVF and egg freezing.
It is important to research each country's specific laws and regulations to ensure that you are fully informed about your options and any potential limitations or restrictions.
You can always speak to our team and consult us to learn more. We are always here to help and provide you with the necessary information.
What is a Care Advocate & how does it benefit me?
Our Care Advocate is a dedicated team member who can help you schedule consultations, appointments, and diagnostic testing.
You can contact our Care Advocate by booking a Discovery Call here.
Is the treatment painful?
We understand that many women may feel apprehensive upon learning about the need for self-administered injections prior to the egg retrieval procedure. However, it's important to note that discomfort rather than moderate-to-severe pain is commonly reported by women throughout the process. Of course, we need to highlight that every individual's pain tolerance level differs.
Rest assured that your doctor will provide detailed information and guidance regarding what to expect before, during, and after the egg freezing process, addressing any concerns you may have. Their expertise will help ensure your comfort and understanding every step of the way.
Treatment: IVF
How long is the IVF process?
All IVF and egg freezing appointments are outpatient procedures, which means you won't need to stay overnight at the clinics. You'll need to take some time off for your egg retrieval during the treatment. However, you can choose whether or not to take time off work for other appointments or procedures as necessary.
We offer appointment scheduling to accommodate your busy schedule.
Do I need to take time off work for IVF?
All IVF and egg freezing appointments are outpatient procedures, which means you won't need to stay overnight at the clinics.
You'll need to take some time off for your egg retrieval during the treatment. However, you can choose whether or not to take time off work for other appointments or procedures as necessary.
We offer appointment scheduling to accommodate your busy schedule.
What is the success rate of IVF?
The success rate of IVF varies depending on several factors, including age, medical history, and treatment type.
What if I don't get pregnant after treatment?
While we don't guarantee any success, our team will work with you to explore additional treatment options if needed and provide emotional support throughout the process.
What are some of the side effects that I may experience?
DURING STIMULATION
Some patients may experience skin changes due to hormonal shifts caused by fertility medications. Acne breakouts are the most common skin changes; others may experience dryness and flakiness. Although it is unpredictable how one's skin will react during the treatment cycle, there are simple steps you can take to prevent or manage such changes. Choosing a gentle, oil-free facial cleanser and moisturiser suited to your skin type is advisable before embarking on an IVF or egg freezing cycle.
Bloating and ConstipationBloating is a common side effect of treatment, which can affect one's appetite due to the limited abdominal space occupied by the ovaries and bloating. Constipation is also a typical bowel change during fertility treatment and is often associated with elevated progesterone levels, which occur after ovulation, egg retrieval, and during pregnancy.
Weight GainWeight gain during fertility treatment is normal due to stress, hormone fluctuations, and bloating. Despite being common, weight gain may still lead to elevated stress, and one should seek ways to manage it.
HeadachesHeadaches can also occur during treatment, especially in patients who frequently experience headaches or migraines. Hormonal changes in the body typically trigger these headaches.
AFTER RETRIEVAL
SorenessAfter the egg-freezing cycle ends, menstrual cycles should return to normal, and any soreness from the egg retrieval should subside within a few days. You may feel some pain upon waking up, such as vaginal soreness or abdominal cramping, similar to period pains. However, such side effects typically last a few days after the procedure. Most women can resume their regular activities, including work, the day after the procedure, although taking a few days off to recuperate is also acceptable.
Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS)In rare cases, ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS) may occur if the egg freezing medications stimulate the ovaries excessively. This condition results in swollen, enlarged ovaries and the accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity. While the chances of OHSS or other egg-freezing severe side effects are minimal, medical professionals monitor patients for signs of such complications throughout the process. If any severe side effects are detected, the doctor will take immediate steps to prevent them.
What are the risks of fertility treatment?
Fertility treatment carries some risks, including the risk of multiple pregnancies, ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome, and ectopic pregnancy. Our team can provide more information based on your specific circumstances.
Can I switch from another fertility clinic to Zora?
We will absolutely love to help. We understand that each patient's situation is unique. Our team is always happy to work with you to develop a personalised plan that meets your needs.
If you have frozen eggs or embryos from another clinic, we can help you coordinate the transfer process to ensure a seamless transition to our partner clinic.
Just give us a call or schedule a consultation to discuss your options.
What is ICSI?
In vitro fertilization (IVF) commonly employs the intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) technique, which involves the injection of a sperm cell directly into the centre of an egg to increase the chances of fertilisation.
Treatment: Egg Freezing
What factors should I consider if I am considering egg freezing?
When considering egg freezing, there are several important factors to keep in mind. The timing of the procedure is a crucial consideration since both eggs and sperm decline in quality and quantity as we age. It is generally recommended to freeze your eggs as early as possible to ensure optimal quality and quantity. While there is a "magic age" of 35 for eggs, it's still recommended to freeze them earlier if possible.
Cost is another important factor to consider. If cost is not a major concern, then freezing your eggs can be a good form of "insurance" as they are frozen at the age you do it. However, it's important to note that egg freezing is not a foolproof method, and there is much debate about its efficacy.
The type of treatment is another consideration to keep in mind. If you are looking to preserve your fertility, you can opt for either egg freezing (for single women) or embryo freezing (for couples). If you are looking to get pregnant, there are various options such as IVF, IUI, and others.
Legalities are also an important factor to consider. Can you do egg freezing in Singapore, for example? Additionally, it's important to think about what happens in the future, as some places only allow married couples to use the frozen eggs.
Finally, logistics must be taken into account. Where do you want to do the procedure? If overseas, would you prefer to do a hybrid process (stimulation in Singapore, retrieval overseas), or spend 2-3 weeks overseas for the entire process? Each option has its own pros and cons that must be weighed carefully.
What is the difference between egg freezing & embryo freezing?
What is egg freezing?
Egg freezing is a procedure that involves collecting a woman’s eggs from her ovaries and freezing them for use in the future.
There are a number of reasons why women may choose to freeze their eggs. Often, women want to preserve their fertility so that they can try and have a family when they are ready at a later date. This is known as ‘social’ egg freezing. Women may also choose to freeze their eggs before undergoing medical treatment that may impact their fertility, such as chemotherapy. When a woman is ready to use the frozen eggs, they are defrosted and fertilised, before being transferred to the womb.
What is embryo freezing?
Embryo freezing is a procedure that allows women to store fertilised eggs for later use. These eggs will have been fertilised in a laboratory with either a partner or donor’s sperm. Most often, when people undergo in vitro fertilisation (IVF) or intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI), good quality embryos are left over after embryo transfer. These embryos can be frozen for use in the future, should the treatment not work or should people wish to try for another baby.
Other people may choose to freeze their embryos to preserve fertility, so they can use them to try to get pregnant at a later date. This is known as the ‘freeze all’ or elective frozen embryo transfer (FET) technique. In certain cases, patients with specific health conditions may benefit from having an FET. Sometimes, embryos are frozen to be donated to others, or for medical research.
Main Difference
The difference between freezing eggs vs. freezing embryos can be found in the lab, too. During embryo freezing, the eggs are fertilized using IVF before they’re frozen, and develop, over a period of several days, into embryos, which are then flash frozen. Once again, the health of the embryos, created from young and healthy eggs, is maintained when they’re frozen at such a low temperature.
Should I go for egg freezing or embryo freezing?
When it comes to comparing freezing eggs versus freezing embryos, egg freezing is often the more practical and flexible choice for many women. Freezing embryos requires fertilization with sperm before freezing, which may not be useful or feasible for single women or those unsure about their co-parenting plans.
1. CONSENT AND AUTONOMY
A key difference between embryo freezing and egg freezing is the issue of autonomy. Eggs can be frozen without needing to be fertilized first, which allows women to preserve their fertility independently and decide what eventually happens to their eggs. With embryo freezing, the embryos belong to two people. If you freeze embryos with donor sperm, you may not be able to use them if you find a partner later and want to have biological children with them.
Additionally, freezing embryos with your current partner may limit your options down the line and even create legal issues if you disagree on how to use or dispose of them.
“With embryo freezing, the embryos belong to two people. This means if you’ve used a partner or private donor’s sperm, they could withdraw consent for the embryos to be used at any time before they are transferred (this does not apply if you’ve used sperm from a donor bank). This means if your circumstances change – a relationship breaks up, for example – you could end up in a situation where you are unable to use the embryos you’ve frozen.” In contrast, freezing eggs offers more reproductive autonomy and the ability to delay co-parenting decisions until you're ready. It's also a simpler path forward in the case of a breakup or divorce, and discarding unfertilized eggs is a more straightforward decision than discarding embryos.
2. COST
Egg freezing is generally more affordable than embryo freezing since the latter requires in vitro fertilization before freezing.
3. SUCCESS RATE
Many people also believe a frozen embryo is more likely to become a pregnancy than a frozen egg. But that’s not a true comparison, statistically speaking. Comparing freezing eggs vs. freezing embryos typically requires several eggs to result in one embryo, no matter which method you choose. You can freeze many eggs, which may be fertilised later to create a few embryos, or, you can fertilize the eggs right after retrieval and freeze the few embryos that develop. Either way, you will likely have the same number of potential chances at pregnancy.
There was a time, using older slow-freeze technology, when embryos survived the freezing and thawing process better than eggs because embryos are slightly less delicate. However, the introduction of vitrification (flash freezing) has largely eliminated this difference. With this state-of-the-art technique, the survival rates when freezing eggs vs freezing embryos are very similar: 90%+ of eggs and about 95% of embryos survive.
Overall, egg freezing is a practical and accessible choice that allows more women to preserve their options for the future. Ultimately, it is still your own choice!
How many eggs should I freeze?
The number of eggs to freeze varies depending on several factors, including age and ovarian reserve.
On average, it takes two egg freezing cycles to reach the recommended number of eggs for optimal chances of pregnancy. While not every frozen egg will result in a successful pregnancy, freezing more mature eggs increases the chances of success.
For women 37 or younger with good ovarian reserve function, it is typically recommended to freeze between 15 to 20 matured eggs. For women over 37 or those with diminished ovarian function, it is recommended to freeze 25 to 30 eggs to provide multiple attempts to conceive.
Your specialist can provide more guidance based on your specific circumstances.
How long can eggs be frozen?
Eggs can be frozen for many years, with some studies suggesting that they can remain viable for up to 10 years or more.
What are some of the side effects that I may experience?
DURING STIMULATION
Some patients may experience skin changes due to hormonal shifts caused by fertility medications. Acne breakouts are the most common skin changes; others may experience dryness and flakiness. Although it is unpredictable how one's skin will react during the treatment cycle, there are simple steps you can take to prevent or manage such changes. Choosing a gentle, oil-free facial cleanser and moisturiser suited to your skin type is advisable before embarking on an IVF or egg freezing cycle.
Bloating is a common side effect of treatment, which can affect one's appetite due to the limited abdominal space occupied by the ovaries and bloating. Constipation is also a typical bowel change during fertility treatment and is often associated with elevated progesterone levels, which occur after ovulation, egg retrieval, and during pregnancy.
Weight gain during fertility treatment is normal due to stress, hormone fluctuations, and bloating. Despite being common, weight gain may still lead to elevated stress, and one should seek ways to manage it.
Headaches can also occur during treatment, especially in patients who frequently experience headaches or migraines. Hormonal changes in the body typically trigger these headaches.
AFTER RETRIEVAL
After the egg-freezing cycle ends, menstrual cycles should return to normal, and any soreness from the egg retrieval should subside within a few days. You may feel some pain upon waking up, such as vaginal soreness or abdominal cramping, similar to period pains. However, such side effects typically last a few days after the procedure. Most women can resume their regular activities, including work, the day after the procedure, although taking a few days off to recuperate is also acceptable.
In rare cases, ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS) may occur if the egg freezing medications stimulate the ovaries excessively. This condition results in swollen, enlarged ovaries and the accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity. While the chances of OHSS or other egg-freezing severe side effects are minimal, medical professionals monitor patients for signs of such complications throughout the process. If any severe side effects are detected, the doctor will take immediate steps to prevent them.
Infertility
What is infertility?
Infertility is defined as the inability to conceive after one year of regular, unprotected sexual intercourse. Because fertility in women is known to decline steadily with age, some providers evaluate and treat women aged 35 years or older after six months of unprotected sex.
Around 17.5% of the adult population – roughly 1 in 6 worldwide – experience infertility.
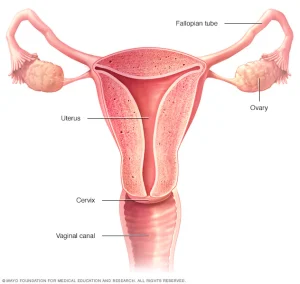
What causes female infertility?
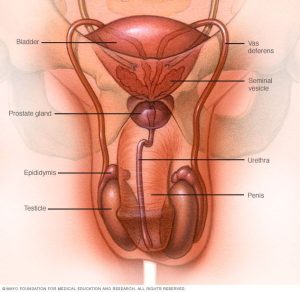
What causes male infertility?
When should I see a doctor?
The main symptom of infertility is not getting pregnant. There may be no other obvious symptoms. Sometimes, women with infertility may have irregular or absent menstrual periods. In some cases, men with infertility may have some signs of hormonal problems, such as changes in hair growth or sexual function.
Women should talk with a care provider earlier, however, if they:
Are age 35 or older and have been trying to conceive for six months or longerAre over age 40Have irregular or absent periodsHave very painful periodsHave known fertility problemsHave been diagnosed with endometriosis or pelvic inflammatory diseaseHave had multiple miscarriagesHave undergone treatment for cancerMen should talk to a health care provider if they have:
A low sperm count or other problems with spermA history of testicular, prostate or sexual problemsUndergone treatment for cancerSmall testicles or swelling in the scrotumOthers in your family with infertility problemsHow long should I try to get pregnant before seeing a doctor?
A woman’s chances of having a baby decrease rapidly every year after age 30. Most experts suggest women younger than age 35 with no apparent health or fertility problems and regular menstrual cycles should try to conceive for at least one year before seeing a doctor. However, for women aged 35 years or older, couples should see a health care provider after 6 months of trying unsuccessfully. Women over 40 years may consider seeking more immediate evaluation and treatment.
Some health problems also increase the risk of infertility. So, couples with the following signs or symptoms should not delay seeing their health care provider when they are trying to become pregnant:
For women:
Irregular periods or no menstrual periodsEndometriosisA history of pelvic inflammatory diseaseKnown or suspected uterine or tubal diseaseA history of more than one miscarriageGenetic or acquired conditions that predispose to diminished ovarian reserve (chemotherapy, radiation)
For men:
A history of testicular traumaPrior hernia surgeryPrior use of chemotherapyA history of infertility with another partnerSexual dysfunction
It is a good idea for any woman and her partner to talk to a healthcare provider before trying to get pregnant. They can help you get your body ready for a healthy baby, answer fertility questions, and give tips on conceiving.
What are some of the risks?
What tests are done to diagnose infertility?
In the usual fertility test,
Fertility tests for women:
Medical history discussion, especially to check for ovulation or menstrual cycle issuesBlood tests to check hormone levels and ovarian reserve (the number of potential eggs remaining in a woman’s ovaries).Pelvic examinationMinimally invasive procedures, such as ultrasound imaging (sonogram) and surgery, to check for structural causes of infertility
Fertility tests for men:
Medical history discussionSemen test
Depending on your situation, rarely your testing may include:
For women:
Hysterosalpingography. Hysterosalpingography (his-tur-o-sal-ping-GOG-ruh-fee) evaluates the condition of your uterus and fallopian tubes and looks for blockages or other problems. X-ray contrast is injected into your uterus, and an X-ray is taken to determine if the cavity is normal and to see if the fluid spills out of your fallopian tubes.Hysteroscopy. Depending on your symptoms, your doctor may request a hysteroscopy to look for uterine disease. During the procedure, your doctor inserts a thin, lighted device through your cervix into your uterus to view any potential abnormalities.Laparoscopy. This minimally invasive surgery involves making a small incision beneath your navel and inserting a thin viewing device to examine your fallopian tubes, ovaries and uterus. A laparoscopy may identify endometriosis, scarring, blockages or irregularities of the fallopian tubes, and problems with the ovaries and uterus.
For Men:
Hormone testing. You may have a blood test to determine your level of testosterone and other male hormones.Genetic testing. Genetic testing may be done to determine whether there's a genetic defect causing infertility.Testicular biopsy. In select cases, a testicular biopsy may be performed to identify abnormalities contributing to infertility or to retrieve sperm for assisted reproductive techniques, such as IVF.Imaging. In certain situations, imaging studies such as a brain MRI, transrectal or scrotal ultrasound, or a test of the vas deferens (vasography) may be performed.Other specialty testing. In rare cases, other tests to evaluate the quality of the sperm may be performed, such as evaluating a semen specimen for DNA abnormalities.What is unexplained fertility?
Unexplained infertility is when fertility testing hasn't found a cause to explain a person or couples infertility. Treatments include fertility medication, lifestyle changes, intrauterine insemination (IUI) and in vitro fertilization (IVF).
What are the risks of fertility treatment?
Fertility treatment carries some risks, including the risk of multiple pregnancies, ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome, and ectopic pregnancy. Our team can provide more information based on your specific circumstances.
What lifestyle factors can affect fertility or IVF success for women?
Your lifestyle and environment can have an impact on your fertility. Research consistently shows that numerous lifestyle factors can affect fertility in women, men, or both, including but not limited to:
Nutrition, weight, sleep quality and exercisePhysical and psychological stressEnvironmental and occupational exposuresCigarette smokingSubstance and drug use and abuseAlcohol and caffeine consumptionMedicationsFor instance, research has found that:
Obesity is linked to lower sperm count and quality in menWomen with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) who have obesity can greatly improve their chances of ovulation and pregnancy by losing 5% of body weightBeing underweight is linked to ovarian dysfunction and infertility in womenStrenuous physical labour and taking multiple medications can reduce sperm count in malesExcessive exercise can affect ovulation and fertility in womenUsing body-building medications or androgens can affect sperm formationSubstance use, including smoking tobacco, using other tobacco products, marijuana use, heavy drinking, and using illegal drugs such as heroin and cocaine, can reduce fertility in both men and womenHigh blood pressure can change the shape of sperm, thereby reducing fertilityRadiation therapy and chemotherapy can cause infertility in females and males. Those who have to undergo these types of treatments may want to consider fertility preservation.Lifestyle factors are modifiable habits and ways of life that can greatly influence overall health and well-being, including fertility.